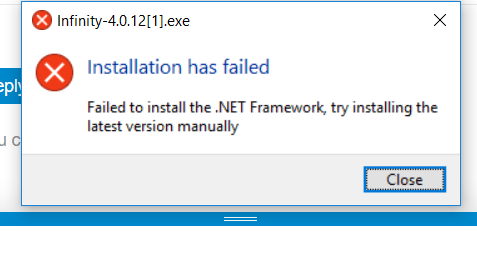
Hresult 0x800f081e
What does DISM Return Code 0x800F081E mean when installing WMF 4.0 on Windows 7 machines? (online) Ask Question Asked 6 years, 1 month ago. Active 6 years, 1 month ago. Pinal Dave is a SQL Server Performance Tuning Expert and an independent consultant. He has authored 12 SQL Server database books, 35 Pluralsight courses and has written over 5400 articles on database technology on his blog at a Along with 17+ years of hands-on experience, he holds a Masters of Science degree and a number of database certifications. Exit Codes for TAEF.; 2 minutes to read; D; a; In this article. The 'Te.exe' command line executable front-end for TAEF returns non-zero exit codes if errors occur during execution. Try downloading the.net 4.8 runtime and see if that works. If this fails, then may I ask if there is a reason you’re still on 1607? There have been three feature releases since that build and it’s already end of life as of April 2019.
-->Group Policy Management is a feature reserved for the Professional, Enterprise, and Education editions of Windows. But with a few tweaks, Home users can enable the Local Group Policy Editor, or you can use a third-party tool to access a more comprehensive collection of settings.
Users can install and run multiple versions of .NET Framework on their computers. When you develop or deploy your app, you might need to know which .NET Framework versions are installed on the user's computer. The registry contains a list of the versions of .NET Framework installed on the computer.
Note
This article is specific to .NET Framework. To determine which .NET Core and .NET 5+ SDKs and runtimes are installed, see How to check that .NET is already installed.
.NET Framework consists of two main components, which are versioned separately:
A set of assemblies, which are collections of types and resources that provide the functionality for your apps. .NET Framework and the assemblies share the same version number. For example, .NET Framework versions include 4.5, 4.6.1, and 4.7.2.
The common language runtime (CLR), which manages and executes your app's code. A single CLR version typically supports multiple .NET Framework versions. For example, CLR version 4.0.30319.xxxxx where xxxxx is less than 42000, supports .NET Framework versions 4 through 4.5.2. CLR version greater than or equal to 4.0.30319.42000 supports .NET Framework versions starting with .NET Framework 4.6.
Community-maintained tools are available to help detect which .NET Framework versions are installed:
A .NET Framework 2.0 command-line tool.
A PowerShell 2.0 module.
For information about detecting the installed updates for each version of .NET Framework, see How to: Determine which .NET Framework updates are installed.
Determine which .NET implementation and version an app is running on
You can use the RuntimeInformation.FrameworkDescription property to query for which .NET implementation and version your app is running on. If the app is running on .NET Framework, the output will be similar to:
By comparison, if the app is running on .NET Core or .NET 5+, the output will be similar to:
Detect .NET Framework 4.5 and later versions
Hresult 0x800f081e
The version of .NET Framework (4.5 and later) installed on a machine is listed in the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full. If the Full subkey is missing, then .NET Framework 4.5 or above isn't installed.

Note
The NET Framework Setup subkey in the registry path does not begin with a period.
The Release REG_DWORD value in the registry represents the version of .NET Framework installed.
| .NET Framework version | Value of Release |
|---|---|
| .NET Framework 4.5 | All Windows operating systems: 378389 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.1 | On Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 378675 On all other Windows operating systems: 378758 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.2 | All Windows operating systems: 379893 |
| .NET Framework 4.6 | On Windows 10: 393295 On all other Windows operating systems: 393297 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.1 | On Windows 10 November Update systems: 394254 On all other Windows operating systems (including Windows 10): 394271 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.2 | On Windows 10 Anniversary Update and Windows Server 2016: 394802 On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 394806 |
| .NET Framework 4.7 | On Windows 10 Creators Update: 460798 On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 460805 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.1 | On Windows 10 Fall Creators Update and Windows Server, version 1709: 461308 On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 461310 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.2 | On Windows 10 April 2018 Update and Windows Server, version 1803: 461808 On all Windows operating systems other than Windows 10 April 2018 Update and Windows Server, version 1803: 461814 |
| .NET Framework 4.8 | On Windows 10 May 2019 Update and Windows 10 November 2019 Update: 528040 On Windows 10 May 2020 Update and Windows 10 October 2020 Update: 528372 On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 528049 |
Minimum version
To determine whether a minimum version of .NET Framework is present, check for a Release REG_DWORD value that's greater than or equal to the corresponding value listed in the following table. For example, if your application runs under .NET Framework 4.8 or a later version, test for a Release REG_DWORD value that's greater than or equal to 528040.
| .NET Framework version | Minimum value |
|---|---|
| .NET Framework 4.5 | 378389 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.1 | 378675 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.2 | 379893 |
| .NET Framework 4.6 | 393295 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.1 | 394254 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.2 | 394802 |
| .NET Framework 4.7 | 460798 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.1 | 461308 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.2 | 461808 |
| .NET Framework 4.8 | 528040 |
Use Registry Editor
From the Start menu, choose Run, enter regedit, and then select OK.
(You must have administrative credentials to run regedit.)
In the Registry Editor, open the following subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full. If the Full subkey isn't present, then you don't have .NET Framework 4.5 or later installed.
Check for a REG_DWORD entry named Release. If it exists, then you have .NET Framework 4.5 or later installed. Its value corresponds to a particular version of .NET Framework. In the following figure, for example, the value of the Release entry is 528040, which is the release key for .NET Framework 4.8.
Use PowerShell to check for a minimum version
Use PowerShell commands to check the value of the Release entry of the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full subkey.
The following examples check the value of the Release entry to determine whether .NET Framework 4.6.2 or later is installed. This code returns True if it's installed and False otherwise.
Query the registry using code
Use the RegistryKey.OpenBaseKey and RegistryKey.OpenSubKey methods to access the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full subkey in the Windows registry.
Important
If the app you're running is 32-bit and running in 64-bit Windows, the registry paths will be different than previously listed. The 64-bit registry is available in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432Node subkey. For example, the registry subkey for .NET Framework 4.5 is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full.
Check the Release REG_DWORD value to determine the installed version. To be forward-compatible, check for a value greater than or equal to the value listed in the .NET Framework version table.
The following example checks the value of the Release entry in the registry to find the versions of .NET Framework 4.5-4.8 that are installed:
The example displays output like the following:
This example follows the recommended practice for version checking:
- It checks whether the value of the Release entry is greater than or equal to the value of the known release keys.
- It checks in order from most recent version to earliest version.
Detect .NET Framework 1.0 through 4.0
Each version of .NET Framework from 1.1 to 4.0 is listed as a subkey at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDP. The following table lists the path to each .NET Framework version. For most versions, there's an Install REG_DWORD value of 1 to indicate this version is installed. In these subkeys, there's also a Version REG_SZ value that contains a version string.
Note
The NET Framework Setup subkey in the registry path does not begin with a period.
| Framework Version | Registry Subkey | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoft.NETFrameworkPolicyv1.03705 | Install REG_SZ equals 1 |
| 1.1 | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv1.1.4322 | Install REG_DWORD equals 1 |
| 2.0 | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv2.0.50727 | Install REG_DWORD equals 1 |
| 3.0 | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv3.0Setup | InstallSuccess REG_DWORD equals 1 |
| 3.5 | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv3.5 | Install REG_DWORD equals 1 |
| 4.0 Client Profile | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Client | Install REG_DWORD equals 1 |
| 4.0 Full Profile | HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv4Full | Install REG_DWORD equals 1 |
Important
If the app you're running is 32-bit and running in 64-bit Windows, the registry paths will be different than previously listed. The 64-bit registry is available in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432Node subkey. For example, the registry subkey for .NET Framework 3.5 is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv3.5.
Notice that the registry path to the .NET Framework 1.0 subkey is different from the others.
Use Registry Editor (older framework versions)
From the Start menu, choose Run, enter regedit, and then select OK.
You must have administrative credentials to run regedit.
Open the subkey that matches the version you want to check. Use the table in the Detect .NET Framework 1.0 through 4.0 section.
The following figure shows the subkey and its Version value for .NET Framework 3.5.
Query the registry using code (older framework versions)
Use the Microsoft.Win32.RegistryKey class to access the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDP subkey in the Windows registry.
Important
If the app you're running is 32-bit and running in 64-bit Windows, the registry paths will be different than previously listed. The 64-bit registry is available in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432Node subkey. For example, the registry subkey for .NET Framework 3.5 is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftNET Framework SetupNDPv3.5.
The following example finds the versions of .NET Framework 1-4 that are installed:
The example displays output similar to the following:
Find CLR versions
The .NET Framework CLR installed with .NET Framework is versioned separately. There are two ways to detect the version of the .NET Framework CLR:
The Clrver.exe tool
Use the CLR Version tool (Clrver.exe) to determine which versions of the CLR are installed on a computer. Open the Developer Command Prompt for Visual Studio and enter
clrver.Sample output:
The
EnvironmentclassImportant
For .NET Framework 4.5 and later versions, don't use the Environment.Version property to detect the version of the CLR. Instead, query the registry as described in Detect .NET Framework 4.5 and later versions.
Query the Environment.Version property to retrieve a Version object.
The returned
System.Versionobject identifies the version of the runtime that's currently executing the code. It doesn't return assembly versions or other versions of the runtime that may have been installed on the computer.For .NET Framework versions 4, 4.5, 4.5.1, and 4.5.2, the string representation of the returned Version object has the form 4.0.30319.xxxxx, where xxxxx is less than 42000. For .NET Framework 4.6 and later versions, it has the form 4.0.30319.42000.
After you have the Version object, query it as follows:
For the major release identifier (for example, 4 for version 4.0), use the Version.Major property.
For the minor release identifier (for example, 0 for version 4.0), use the Version.Minor property.
For the entire version string (for example, 4.0.30319.18010), use the Version.ToString method. This method returns a single value that reflects the version of the runtime that's executing the code. It doesn't return assembly versions or other runtime versions that may be installed on the computer.
The following example uses the Environment.Version property to retrieve CLR version information:
The example displays output similar to the following:
See also
-->The 'Te.exe' command line executable front-end for TAEF returns non-zero exit codes if errors occur during execution. There are different ways in which 'errors' can occur and the process exit code reflects that.
.net 4.7.2 Hresult 0x800f081e
The process exit code from Te.exe is a 32-bit number, and different bits within that number reflect different types of errors. The exit code is broken down as follows:
- Bits 0-15: The 'Test Result value' - this is the number of non-passing tests.
- Bits 16-23: The 'TestMode result value' - the error from the TestMode (not yet used).
- Bits 24-30: The 'Harness result value' - the error from the harness itself.
The most significant bit (bit 31, the sign bit for signed numbers) is not used to avoid signed/unsigned confusion. The process exit code is always positive. More practically stated:
- If the exit code is less than or equal to 0xFFFF (65535), then that is the number of non-passing tests (failed, blocked, not run, or skipped) that Te.exe executed. If more that 65535 tests didn't pass, then the value is capped at 65535.
- If the exit code is larger than 0xFFFF/65535 then something went wrong other than the test code that was being executed.
The following list shows the current 'Harness Result Values' and their interpretation.
| Harness Result Value | Te.exe Exit Code | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0x01000000 (16777216) | Help was requested ('/?' or '/!') - no tests were executed. |
| 2 | 0x02000000 (33554432) | Wex.Logger reported an error. |
| 3 | 0x03000000 (50331648) | Wex.Logger couldn't be initialized. |
| 4 | 0x04000000 (67108864) | Wex.Logger generated invalid Pass/Fail counts (typically unbalanced StartGroup/Engroup calls from a test) |
| 5 | 0x05000000 (83886080) | Invalid command line (no valid test files were specified, '/inproc' specified with multiple Test Files). |
| 6 | 0x06000000 (100663296) | Some other exception occurred. |
| 7 | 0x07000000 (117440512) | No tests were executed. |
| 8 | 0x08000000 (134217728) | TAEF session timed out. |
| 9 | 0x09000000 (150994944) | Version information was requested ('/version') - no tests were executed. |